Lernen Durch Digitale Spiele
Verbundvorhaben zwischen dem Institut für Geographiedidaktik (UzK) und dem Cologne Game Lab (TH-Köln)



Das Ziel
Mündigkeit durch digitale Spiele: Untersuchung der Potentiale und Grenzen von digitalen Spielen für das Treffen mündiger Entscheidungen im Kontext gesellschaftlicher Herausforderunge und deren Reflexion im Geographieunterricht
Ausgewählte aktuelle geographische Themenfelder:

Migration

Klimawandel

Stadtentwicklung

Ressourcennutzung
Vorgehen
Analyse
Analyse von digitalen Spielen, die gesellschaftliche Herausforderungen thematisieren; anschließende Experteninterviews mit SpieleentwicklerInnen

Interviews
Beobachtungen von und qualitative Interviews mit SpielerInnen sowie qualitative Interviews mit Lehrkräften

Leitfäden
Entwicklung eines didaktischen Leitfadens für den Einsatz im Geographieunterricht sowie eines Leitfadens für SpieleentwicklerInnen.

Über Das Projekt
(German Only)
Anforderungen an die Spiele:
01.
Behandeln minimum eins der geographischen Themen.
02.
Hoher Bekanntheitsgrad.

Aktive Team Mitglieder

Alexandra Budke
Alexandra Budke ist Professorin für Humangeographie und ihre Didaktik am
Institut für Geographiedidaktik der Universität zu Köln. Wichtige
Forschungsfelder sind die Argumentation, die Politische Bildung, das
Interkulturelle Lernen und der Einsatz digitaler Medien im
Geographieunterricht.

Emmanuel Guardiola
Emmanuel Guardiola ist Professor für Spieledesign an der Cologne Game Lab. Er hat an mehr als 30 bedeutenden Titeln der Spielebranche mitgewirkt. Er promovierte in Informatik und forscht am CNAM-Labor für Informatik (Paris) über das spielerpsychologische Profiling.

Joelle-Denise Lux
Joelle-Denise Lux ist Doktorandin am Institut für Geographiedidaktik
der Universität zu Köln. Für ihre Dissertation zum Einsatz von Spielen
im Geographieunterricht verbindet sie ihre akademischen Hintergründe
in Geographie und Multimediadesign. Besonderer Schwerpunkt ihrer
Forschung liegt derzeit auf einer Förderung von Systemkompetenz im
Kontext aktueller gesellschaftlich-ökologischer Herausforderungen
mithilfe digitaler Strategiespiele.

André Czauderna
André Czauderna ist wissenschaftlicher Mitarbeiter am Cologne Game Lab der TH Köln, wo er u.a. für das Management und die Weiterentwicklung der Studiengänge BA und MA Digital Games zuständig ist. Außerdem unterrichtet er Media and Game Studies und forscht zu Lernprozessen in Strategie- und Managementspielen, Gaming Affinity Spaces und hochschulischer Games-Ausbildung. Er promovierte in Erziehungswissenschaft an der Johannes Gutenberg-Universität Mainz.
Vergangenheit
Games Versus Reality? How Game Designers Deal with Current Topics of Geography Education
Lux, J.-D.; Budke, A.; Guardiola, E. Games Versus Reality? How Game Designers Deal with Current Topics of Geography Education. In: Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2021, 5, 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti511
Digital entertainment games frequently address current societal issues that are also dealt with in geography education, such as climate change or sustainable city development, and give various opportunities for learning. However, in order to be fully able to determine the games’ educational potential and to instruct meaningful reflection on them in class, the designers’ approaches to realism regarding these topics need to be understood. Therefore, we have developed a model of realism in games and conducted 9 interviews with 10 experts from the entertainment game industry about their understanding of and dealing with realism concerning the represented geographical topics. In many cases, the interviewees’ approach to incorporating real-world issues can be regarded as beneficial for their games’ educational potential, and some designers even pursued learning goals. However, we also identified approaches that can result in questionable presentations of real societal issues. We found the most problematic one to be the prioritization of player expectations for the sake of perceived realism. This approach may lead to the depiction of stereotypes and common misconceptions. The results presented in our study may help teachers to prepare reflection on such misrepresentations in class, or designers to become more aware of the educational implications of different forms of game realism
How Insights into Commercial Games Can Improve the Design of Educational Games on Complex Societal Problems
Czauderna, A., Guardiola, E., Lux, J-D., Budke, A. (2021): How insights into commercial games can improve the design of educational games on complex societal problems. In: Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Games Based Learning: ECGBL, Academic Conferences and Publishing International, pp. 170-177. doi:
10.34190/GBL.21.119
Many educational games have been criticized for their lack of enticement to players, which is attributed, among other factors, to a low degree of complexity and a limited amount of choices, when compared to entertainment games (Sanford et al., 2015). From the perspective of learning theory, this is insofar problematic as successful processes of learning require player motivation, great agency, and a well-balanced level of complexity, which correspondents and adapts to players’ knowledge and skills (Gee, 2007). We thus assume that educational game design can learn from entertainment games, i.e., must look at them in order to improve educational games when it comes to their allure, their simulation/moderation of complexity, and their enabling of meaningful choices. With this in mind, we conducted a series of studies on commercially successful and critically acclaimed simulation and strategy games such as Cities: Skylines, Civilization VI: Gathering Storm, and Tropico 6 referring to the topics of climate change, urban planning, migration, and/or resource management – from the perspective of geography education. Our research focused on different aspects such as the games’ realism, complexity, geographical topics, facilitation of decision-making, and principles of political education, utilizing 18 game analyses and 8 qualitative interviews with game designers of these games. Based on the results of these studies, the present paper derives seven recommendations for the design of games on complex societal problems that can be used for educational purposes in geography education. Overall, the paper contributes to the greater effort to bridge the gap between entertainment game design and educational game design, thereby facilitating the creation of games that are both motivational and educational.
Guidelines for the Design of (educational) Digital Games on Complex Societal Issues
Lux, Joelle-Denise, André Czauderna, Emmanuel Guardiola, und Alexandra Budke (2021): Guidelines for the Design of (Educational) Digital Games on Complex Societal Issues. SocArXiv. June 18. doi: 10.31235/osf.io/9fq4u.
Designers of digital entertainment games and designers of games for education can learn from each other when it comes to gameplay mechanics, content and mediation techniques that enable a fun and at the same time educational experience for players. The following design guidelines bring together the perspectives of entertainment game industry and educators. Based on a range of studies, they present 11 recommendations to facilitate the design of games on complex social and socio-ecological issues such as climate change, migration, city development and resource conflicts – suitable for any designer who wants to provide an enriching game experience.
Game Designer als Akteure der politischen Bildung
Czauderna, André, und Alexandra Budke. 2021. „Game Designer als Akteure der politischen Bildung“. MedienPädagogik: Zeitschrift für Theorie und Praxis der Medienbildung 38 (Aneignung politischer Information): 94-116. https://doi.org/10.21240/mpaed/38/2021.01.25.X.
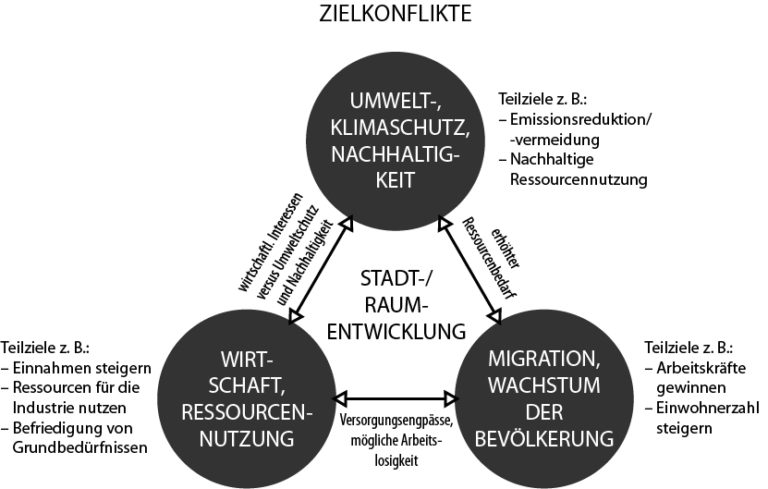
Viele digitale Spiele enthalten – auch wenn sie primär für Unterhaltungszwecke konzipiert wurden – Anknüpfungspunkte für die politische Bildung. So erlauben sie z. B. ihren Spielerinnen und Spielern, in die Rolle politischer Entscheidungsträger zu schlüpfen und sich mit Themen wie Stadtentwicklung, Migration, Ressourcenkonflikte oder Klimawandel zu beschäftigen, welche u. a. für die politische Bildung im Geographieunterricht eine wichtige Rolle spielen. Es ist dementsprechend konsequent, ihre Designerinnen und Designer nicht nur als Akteurinnen und Akteure der Kulturindustrie, sondern auch als solche der politischen Bildung anzusehen. Der vorliegende Beitrag rekonstruiert aus medienpädagogischer und geographiedidaktischer Perspektive mithilfe einer qualitativen Inhaltsanalyse von neun leitfadengestützten Interviews mit Game Designerinnen und Designern von Unterhaltungsspielen, wie diese ihre Rolle als Akteurinnen und Akteure der politischen Bildung wahrnehmen. Insbesondere wird herausgearbeitet, dass ihre Haltung zum Design politischer Entscheidungssituationen weitgehend an den Massstäben des Beutelsbacher Konsenses – d. h. dem Überwältigungsverbot, dem Kontroversitätsgebot und der Interessenorientierung – gemessen werden kann. Gleichwohl muss der Einsatz kommerzieller Spiele in der politischen Bildung in jedem Einzelfall kritisch reflektiert und pädagogisch begleitet werden. Da sich ihre Designerinnen und Designer in ihrer Rolle als Akteurinnen und Akteure der Kulturindustrie – die keinen Bildungsauftrag, aber Kunstfreiheit umfasst – in erster Linie der Unterhaltung ihrer Zielgruppe verpflichtet fühlen müssen, können ihre Produkte nicht genauso streng nach didaktischen Kriterien bewertet werden wie speziell für die politische Bildung erstellte Materialien. Eine kritische Reflexion der Spiele in der politischen Bildung sollte sich u. a. auch dem von den meisten Designerinnen und Designern selbst gesehenen «Demokratiedefizit» der Spiele, das sich z. B. in der Vernachlässigung der intersubjektiven Aushandlung von Entscheidungen darstellt, widmen.
How Digital Strategy and Management Games can Facilitate the Practice of Dynamic Decision-Making
Czauderna, André und Budke, Alexandra (2020): How Digital Strategy and Management Games Can Facilitate the Practice of Dynamic Decision-Making. In: Education Sciences, 10 (4), pp.1-24. https://www.mdpi.com/2227-7102/10/4/99/pdf
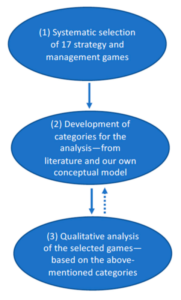
This paper examines how digital strategy and management games that have been initially designed for entertainment can facilitate the practice of dynamic decision-making. Based on a comparative qualitative analysis of 17 games—organized into categories derived from a conceptual model of decision-making design—this article illustrates two ways in which these games may be useful in supporting the learning of dynamic decision-making in educational practice: (1) Players must take over the role of a decider and solve situations in which players must pursue different conflicting goals by making a continuous series of decisions on a variety of actions and measures; (2) three of the features of the games are considered to structure players’ practice of decision-making and foster processes of learning through the curation of possible decisions, the offering of lucid feedback and the modification of time. This article also highlights the games’ shortcomings, from an educational perspective, as players’ decisions are restricted by the numbers of choices they can make within the game, and certain choices are rewarded more than others. An educational application of the games must, therefore, entail a critical reflection of players’ limited choices inside a necessarily biased system.
![Figure 1. Model of decision-making design in digital games (own illustration, including an adapted depiction of the gameplay loop from Salen/Zimmerman [12], p.316](https://dispielgeo.de/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/education-10-00099-g001-300x209.png)

Playing with Complex Systems? The Potential to Gain Geographical System Competence through Digital Gaming
Lux, Joelle-Denise und Budke, Alexandra (2020): Playing with Complex Systems? The Potential to Gain Geographical System Competence through Digital Gaming. In: Education Sciences, 10(5), 130. https://www.mdpi.com/2227-7102/10/5/130/pdf
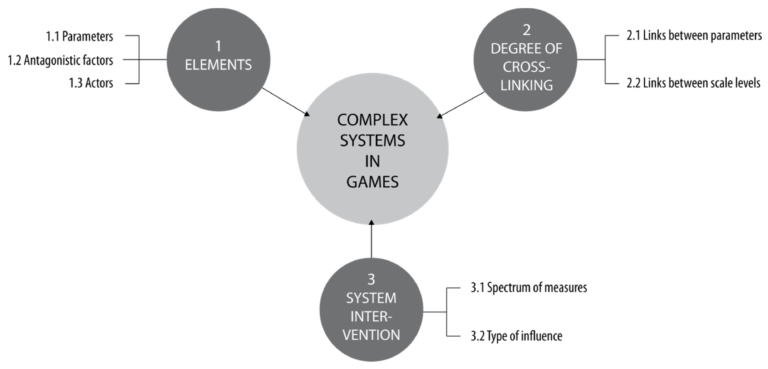
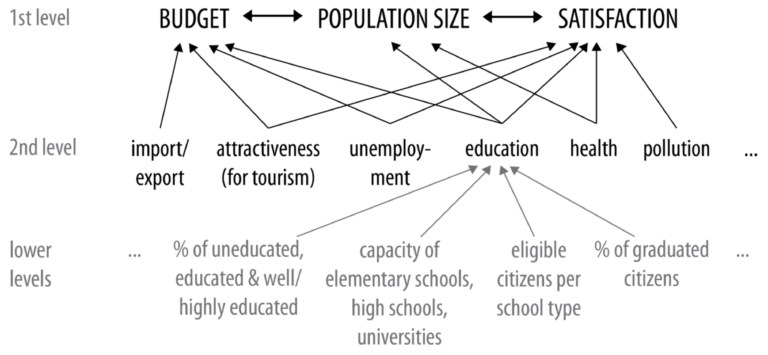
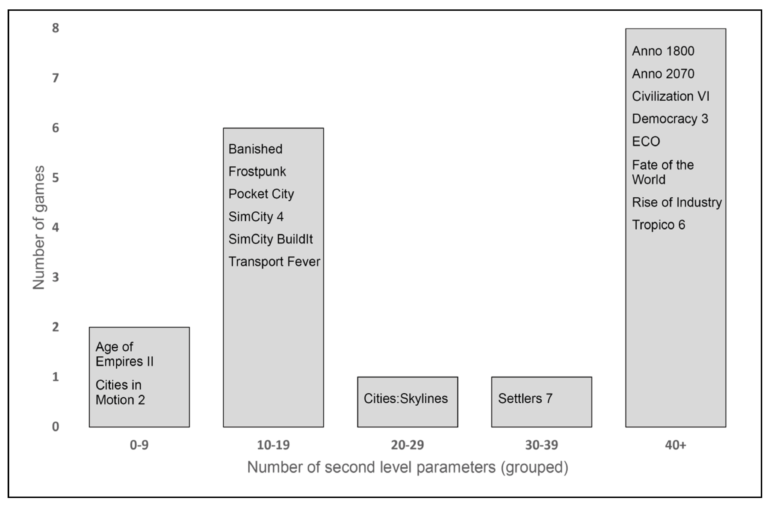
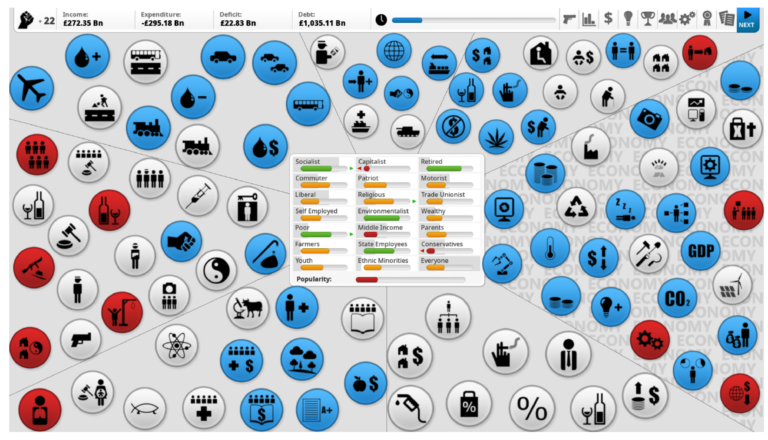
The current socio-ecological challenges and phenomena that are major topics of geography education, like climate change and migration, are highly complex. Maturity in these contexts requires a networked way of thinking, and a systemic competence that is difficult to develop in geography classes alone. Digital games that simulate complex systems which include the pressing issues of today’s challenges may be a useful supplement to foster systems thinking. In this study, we develop a framework to assess the complexity of in-game systems. A subsequent analysis of a selection of current commercial strategy and simulation games shows how system complexity is designed differently in the various games. Based on these results, we make recommendations for the selection and use of different games in formal and informal learning contexts.
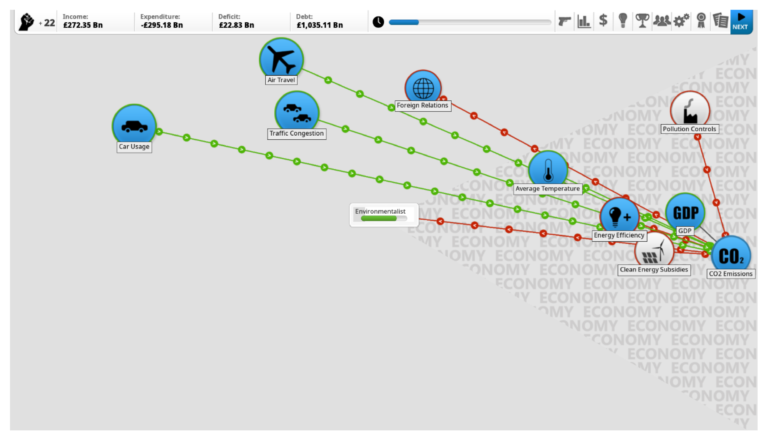
Alles nur ein Spiel? Geographisches Fachwissen zu aktuellen gesellschaftlichen Herausforderungen in digitalen Spielen
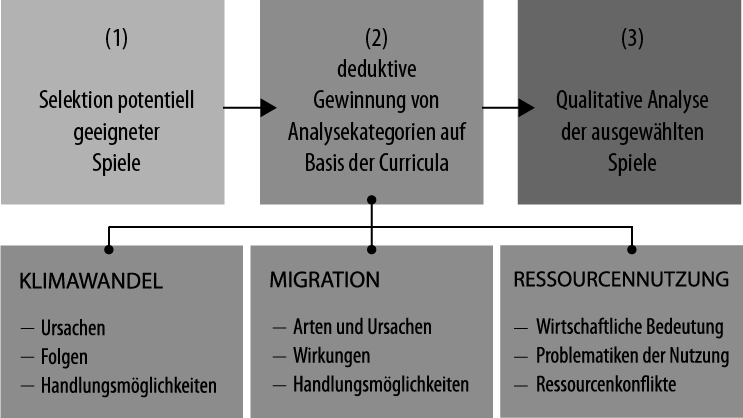
Lux, Joelle-Denise und Budke, Alexandra (2020): Alles nur ein Spiel? Geographisches Fachwissen zu aktuellen gesellschaftlichen Herausforderungen in digitalen Spielen. In: GW-Unterricht 160 (4/2020), 22-36. https://doi.org/10.1553/gw-unt
Trotz besonderer Potentiale von digitalen Unterhaltungsspielen für die Bildung finden diese bislang kaum Anwendung im Geographieunterricht, was an mangelnder Kenntnis über deren fachliche Relevanz liegen könnte. Die vorliegende Studie versucht Potentiale und Grenzen kommerzieller Strategie- und Simulationsspiele für den Kompetenzbereich Fachwissen im Geographieunterricht herauszuarbeiten, insbesondere für aktuelle gesellschaftliche Themen. Unsere Spieleanalyse zeigt, dass besonders in den Themen Klimawandel und Ressourcennutzung viele lehrplanrelevante Aspekte dargestellt werden und die aktive Problemlösefähigkeit von Spielerinnen und Spielern gefördert wird, aber dass die Spiele auch einige Systemzusammenhänge vereinfachen, was im Unterricht reflektiert werden sollte.
Modell für Erfolgsbedingungen
&
Leitlinien
für Lehrkräfte und Spieleentwickler

Für LehrerInnen
Erfolgsmodell Bedingungen und Leitlinien für Lehrkräfte für den Einsatz digitaler Spiele im Geografieunterricht.

Für Game DesignerInnen
Modell für Erfolgsbedingungen und Leitlinien für die Gestaltung von (pädagogischen) digitalen Spielen zu komplexen gesellschaftlichen Themen.
Mehr zum Projekt
Poster